在分布式系统中,雪花算法(Snowflake)生成的ID无疑是我们的得力助手。但当我们面对这样一长串数字时:1234567890123456789,是否曾感到它在URL、二维码或用户界面中显得过于“臃肿”?
我们如何在保持其分布式优势的同时,让它变得短小精悍?本文将带你深入Base62编码的奇妙世界。
一、痛点:当长ID遇上短场景
想象一下这些场景:
- 短链接服务:
https://example.com/aB3dEfGh远比 https://example.com/1234567890123456789优雅
- 二维码内容:更短的字符串意味着更简单的二维码图案
- 用户界面展示:用户分享时,短ID更容易记忆和传播
- API参数:URL参数更简洁,降低请求长度
传统方案可能会使用UUID或自增ID,但它们各有弊端。雪花ID虽然解决了分布式唯一性问题,却带来了“过长”的新问题。
二、解决方案:Base62编码的精妙之处
- 为了解决上面的问题,我们写一个工具类,可以把数字ID,转为短的字符串表示,有一种算法是Base62编码算法——这是一种使用62个字符(a-z、A-Z、0-9)表示数字的编码方式。
为何是Base62,而不是Base64?
- URL友好:Base64中的
+和/在URL中需要转义,Base62则完全安全
- 字符集精简:62个字符既保证了编码效率,又保持了可读性
- 如果你觉得容易混淆的字符(如
0和O,1和l)也可以去掉,那就是Base58 算法
- 我们来看看代码实现
三、代码深度解析
1、核心数据结构
1
2
3
|
private static final String BASE_CHARS =
"rstyoabcdefghijklmnpquvwxz0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
|
- 这个字符串是可以随意打乱顺序的哈,这种就避免人家知道你的base62算法然后进行解码。
- 也可以把如
0和O,1和l 这种容易看错的去掉,避免混淆
- 编码的核心逻辑在
encode方法中:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| private static final char[] CHAR_SET = BASE_CHARS.toCharArray();
public static String encode(long id) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (id > 0) {
int remainder = (int)(id % BASE);
sb.append(CHAR_SET[remainder]);
id = id / BASE;
}
return sb.reverse().toString();
}
|
- 这个过程就像将十进制数转换为62进制,但使用的是我们自定义的字符集。
- 举个简单例子:
- 十进制
123→ 62进制:123 ÷ 62 = 1 余 61
- 余数61对应字符
Z,商1对应字符s
- 最终得到
sZ(反转后)
这个例子是以我上面的Base62字符集来举例的,得到的
2、固定长度编码:统一格式的美学
在实际应用中,我们常常希望ID长度固定,便于对齐和存储:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
private static final char PADDING_CHAR = CHAR_SET[0];
public static String encodeFixed(long id, int minLength) {
String encoded = encode(id);
if (encoded.length() < minLength) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < minLength - encoded.length(); i++) {
sb.append(PADDING_CHAR);
}
sb.append(encoded);
return sb.toString();
}
return encoded;
}
|
例如,ID123转换为固定8位:rrrrrrsZ。
3、解码:从短字符串还原长整型
解码是编码的逆过程,核心是加权求和:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| private static final Map<Character, Integer> CHAR_INDEX_MAP = new HashMap<>();
static {
for (int i = 0; i < BASE; i++) {
CHAR_INDEX_MAP.put(CHAR_SET[i], i);
}
}
public static long decode(String shortId) {
long id = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < shortId.length(); i++) {
char c = shortId.charAt(i);
int digit = CHAR_INDEX_MAP.get(c);
id = id * BASE + digit;
}
return id;
}
|
4、完整代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
| import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class SnowflakeIdConverter {
private static final String BASE_CHARS = "rstyoabcdefghijklmnpquvwxz0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
private static final char[] CHAR_SET = BASE_CHARS.toCharArray();
private static final int BASE = CHAR_SET.length;
private static final Map<Character, Integer> CHAR_INDEX_MAP = new HashMap<>();
public static final int DEFAULT_FIXED_LENGTH = 8;
private static final char PADDING_CHAR = CHAR_SET[0];
static {
for (int i = 0; i < BASE; i++) {
CHAR_INDEX_MAP.put(CHAR_SET[i], i);
}
}
public static String encode(long id) {
if (id < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("ID必须是正数");
}
if (id == 0) {
return String.valueOf(CHAR_SET[0]);
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (id > 0) {
int remainder = (int)(id % BASE);
sb.append(CHAR_SET[remainder]);
id = id / BASE;
}
return sb.reverse().toString();
}
public static String encodeFixed(long id, int minLength) {
if (minLength <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("固定长度必须大于0");
}
String encoded = encode(id);
if (encoded.length() > minLength) {
return encoded;
}
if (encoded.length() < minLength) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < minLength - encoded.length(); i++) {
sb.append(PADDING_CHAR);
}
sb.append(encoded);
return sb.toString();
}
return encoded;
}
public static String encodeFixed(long id) {
return encodeFixed(id, DEFAULT_FIXED_LENGTH);
}
public static long decodeFromFixed(String fixedId) {
if (fixedId == null || fixedId.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("字符ID不能为空");
}
String cleanedId = removePaddingChars(fixedId);
if (cleanedId.isEmpty()) {
return 0;
}
return decode(cleanedId);
}
private static String removePaddingChars(String str) {
int start = 0;
while (start < str.length() && str.charAt(start) == PADDING_CHAR) {
start++;
}
return str.substring(start);
}
public static long decode(String shortId) {
if (shortId == null || shortId.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("字符ID不能为空");
}
long id = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < shortId.length(); i++) {
char c = shortId.charAt(i);
if (!CHAR_INDEX_MAP.containsKey(c)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("输入字符串中的字符无效: " + c);
}
int digit = CHAR_INDEX_MAP.get(c);
id = id * BASE + digit;
}
return id;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
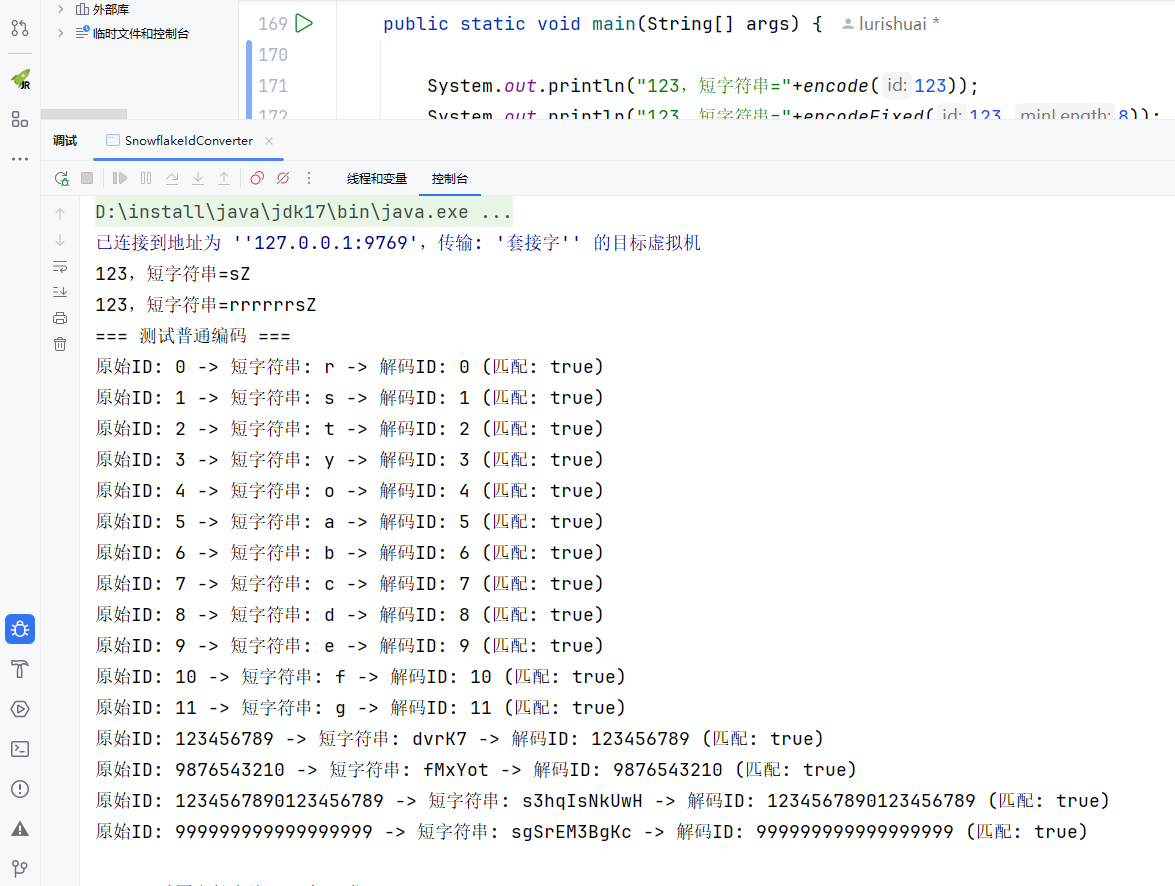
System.out.println("123,短字符串="+encode(123));
System.out.println("123,短字符串="+encodeFixed(123,8));
long[] testIds = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 123456789L, 9876543210L, 1234567890123456789L, 999999999999999999L};
System.out.println("=== 测试普通编码 ===");
for (long id : testIds) {
String shortId = encode(id);
long decodedId = decode(shortId);
System.out.println("原始ID: " + id +
" -> 短字符串: " + shortId +
" -> 解码ID: " + decodedId +
" (匹配: " + (id == decodedId) + ")");
}
System.out.println("\n=== 测试固定长度编码(默认8位)===");
for (long id : testIds) {
try {
String fixedId = encodeFixed(id);
long decodedId = decodeFromFixed(fixedId);
System.out.println("原始ID: " + id +
" -> 固定长度字符串[" + fixedId.length() + "]: " + fixedId +
" -> 解码ID: " + decodedId +
" (匹配: " + (id == decodedId) + ")");
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
System.out.println("原始ID: " + id + " -> 错误: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
|
四、应用场景
1、场景1:邀请码
- 大部分应用的用户ID,基本都是数字的,有些是数据库自增id,有些是类似雪花算法的那种长整型,如果我们需要给每个用户设置一个专属他的邀请码不就可以直接通过他的ID转为字符串即可。唯一不重复且可以解码得到用户ID。
- 还有,如果我们用户的ID使用的是数据库自增ID,我们也可以返回这种编码后的id给前端,避免被遍历爬取用户信息或暴露用户量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public static String generateInviteCode(Long userId) {
long saltedId = userId ^ 0x12345678L;
return SnowflakeIdConverter.encodeFixed(saltedId, 8);
}
public static Long parseUserId(String inviteCode) {
long saltedId = SnowflakeIdConverter.decode(inviteCode);
return saltedId ^ 0x12345678L;
}
|
2、场景2:订单号优化
- 相同的订单号的展示是不是也和上面一样的,传统的订单号可能是
202512111234567890
1
2
3
| long orderId = 202512111234567890L;
String shortOrderNo = SnowflakeIdConverter.encodeFixed(orderId, 10);
|
3、场景3:短链接服务
- 大家手机有时候都会收到垃圾短信,然后短信内容有时候会有一个很短的
蓝色可点击的短链接吧,那种就是短链接了。
- 当我们点击短的链接时,请求到服务器,服务器就会解析短链接地址得到真实的访问URL地址,然后重定向到正式地址。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public String generateShortUrl(long snowflakeId) {
String shortCode = SnowflakeIdConverter.encodeFixed(snowflakeId, 6);
return "https://short.url/" + shortCode;
}
public long parseShortUrl(String shortUrl) {
String code = shortUrl.substring(shortUrl.lastIndexOf("/") + 1);
return SnowflakeIdConverter.decodeFromFixed(code);
}
|
五、总结
通过SnowflakeIdConverter工具类,我们实现了:
- 空间压缩:将19位的长整型压缩为平均6-11位的字符串
- 双向转换:完全可逆,不丢失信息
- 配置灵活:支持固定长度、自定义字符集
在当今的微服务、分布式系统架构下,这样的工具类具有广泛的实用价值。它不仅简化了ID的展示和传输,更为用户体验带来了实实在在的提升。
技术不是目的,而是手段。好的工具类应该像这个ID转换器一样:解决实际问题,保持简单优雅,兼顾性能与扩展。希望这个工具类和解析能对你在实际开发中有所启发和帮助。
欢迎分享你的经验:
在实际工作中,你有哪些独到的见解或踩坑经验?欢迎在评论区交流讨论,让我们一起进步
关注我,获取更多实战技术干货。



